Recap on system design for this week:
REST API Architecture style
Caching strategies Part 1 (5 strategies)
Differences Between API Gateway and Load Balancer
Linux commands. Part 1 (37 commands)
Diagram as Code
1. REST API Architecture style

1.1. Message formats:
XML
JSON
Other
1.2. ✅ Advantages:
Stateless: Scales easily
Cacheable: Improved performance
Uniform Interface: Standardized use
Scalable: Supports high request volumes
Interoperable: Works well with HTTP
Simple: Uses standard HTTP methods
Widely Adopted: Many resources available
1.3. ❌ Disadvantages
Over/Under-fetching: Fixed data returns
Multiple Endpoints: More requests for complex data
Versioning Issues: Changes can break clients
Limited Flexibility: Fixed data structures
Performance: Multiple trips for complex data.
Stateful Limitations: Not ideal for real-time operations
Nested Resource Complexity: Harder to manage nested data
1.4. 📋 Use cases
Web Applications. Backend for web apps with CRUD operations.
Mobile Apps. Backend support for mobile app data needs.
Public APIs. Offer services to third-party developers.
Integration. Connect different systems or services.
Content Delivery. Distribute content to various platforms.
Data Storage. Backend for apps needing database access.
E-Commerce. Manage products, orders, and user accounts.
Social Media Platforms. Handle user data, posts, and interactions.
IoT Devices. Communicate with and manage IoT devices.
Legacy System Interface. Modern interface for older systems.
❓ What API architecture style are you guys currently utilizing in your system?
2. Caching strategies: Cache Aside (Lazy Loading), Read-Through, Write-Through, Write-Around, Write-Behind (Write-Back)
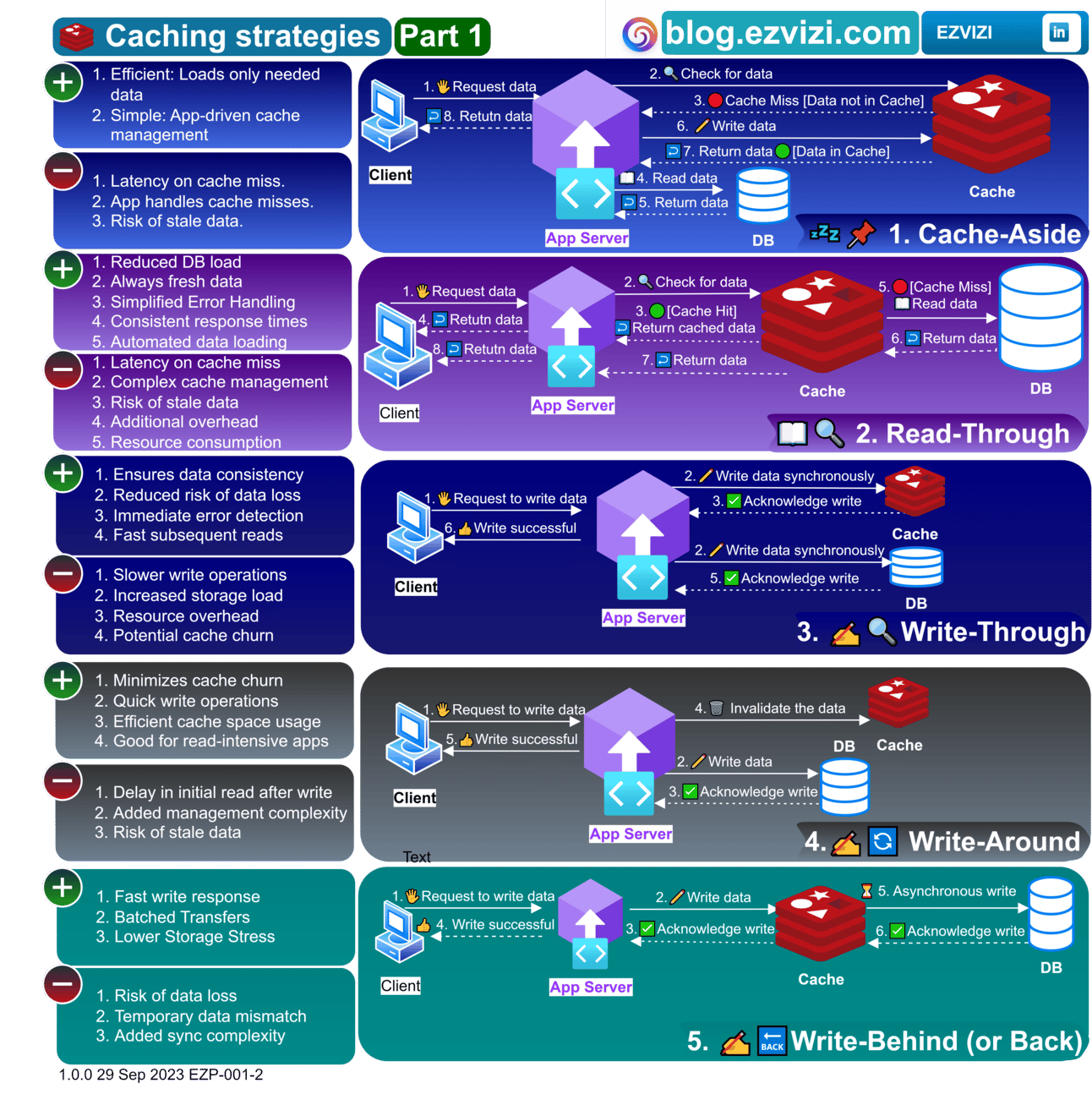
2.1. 💤📌Cache-Aside (Lazy Loading)
Data is loaded into the cache on demand. If data is not found in the cache, the application retrieves it from the datastore and then stores it in the cache.
Pros:
🎯 Only requested data is cached.
🔄 Cache can be easily refreshed.
Cons:
❌ Initial cache miss incurs a latency penalty.
🔄 Manual intervention required for cache updates.
2.2. 📖🔍Read-Through
The cache is responsible for loading data from the datastore when a cache miss occurs.
Pros:
🔄 Automatic data loading.
🎯 Consistent cache and datastore data.
Cons:
❌ Initial cache miss can slow down the application.
2.3. ✍️🔍Write-Through
Data is written to both the cache and the datastore synchronously (simultaneously).
Pros:
✅ Immediate data consistency.
🔄 Automatic data updates.
Cons:
❌ Slower write operations due to dual writes.
2.4. ✏️🔄 Write-Around
Data is written directly to the datastore, bypassing the cache. The cache is updated later or during subsequent read operations.
Pros:
⚡ Faster initial write operations.
🎯 Reduces cache churn for less frequently accessed data.
Cons:
❌ Subsequent reads might suffer from cache misses.
2.5. ✏️🔙Write-Behind (Write-Back)
Data is first written to the cache, and then asynchronously written to the datastore.
Pros:
⚡ Fast write operations.
🔄 Asynchronous updates optimize datastore writes.
Cons:
❌ Risk of data loss if cache fails before async write.
❓ What combination of caching strategies are you guys currently implementing in your system?
3. Differences Between API Gateway and Load Balancer

While both API Gateways and Load Balancers manage incoming requests, they serve different primary roles. In many architectures, especially in microservices, you'll often find both an API gateway and a load balancer working in tandem. An API Gateway focuses on API management, offering a suite of tools for processing and directing API calls. In contrast, a Load Balancer's main job is to distribute traffic to ensure optimal server performance and availability.
API Gateway: 🌐 Primary Role: Manages and processes API requests.
🔹 Functions:
🚦 Request Routing: Directs requests to the appropriate service.
🧩 API Composition: Aggregates data from multiple services.
⏳ Rate Limiting: Limits request frequency.
🔒 Security: Manages authentication and API keys.
🚀 Caching: Improves response times with stored data.
🔄 Request/Response Transformation: Modifies data formats.
📊 Analytics & Monitoring: Tracks API usage.
🔍 Service Discovery: Identifies available services.
❌ Error Handling & Retry: Manages failed requests.
🔧 Protocol Translation: Converts communication protocols.
🔹 Use Cases: Microservices, API management, data aggregation, securing APIs.
Load Balancer: ⚖️ Primary Role: Distributes incoming network traffic.
🔹 Functions:
🌊 Traffic Distribution: Prevents server overloads.
❤️ Health Checks: Monitors server health.
🔐 SSL Termination: Handles SSL/TLS processing.
🧬 Session Persistence: Maintains client-server connection.
📡 Layer 4 and Layer 7 Load Balancing: Operates at transport and application layers.
🔹 Use Cases: High availability, fault tolerance, application scaling, large-scale web traffic management.
Key Differences:
🎯 Focus: API gateway = API management. Load balancer = traffic distribution.
🔍 Granularity: API gateway = fine-grained control. Load balancer = broader network level.
🛠️ Features: API gateway = tailored for API management. Load balancer = traffic and health management.
In modern architectures, especially microservices, both API gateways and load balancers often work together. The load balancer manages traffic, while the API gateway handles API requests.
❓ Are you guys utilizing both API gateways and load balancers in your infrastructure?
4. Linux commands. Part 1 (37 commands).

File Operations 📂:
ls📄: List directory contentsExample:
ls -l
cp📋: Copy files and directoriesExample:
cp source.txt destination.txt
mv🚚: Move or rename files and directoriesExample:
mv oldname.txt newname.txt
rm🗑️: Remove files or directoriesExample:
rm unwanted.txt
touch✍️: Create an empty fileExample:
touch newfile.txt
cat📖: Concatenate and display file contentExample:
cat file.txt
Directory Operations 📁:
pwd📍: Print working directoryExample:
pwd
cd🚪: Change directoryExample:
cd /home/user/documents
mkdir🆕📁: Make directoriesExample:
mkdir new_directory
rmdir🚫📁: Remove empty directoriesExample:
rmdir empty_directory
System Info ℹ️:
uname🖥️: Display system informationExample:
uname -a
top📊: Display system tasksExample:
top
df💽: Disk space usage of file systemExample:
df -h
free🧠: Display memory usageExample:
free -m
ps🔄: Display process statusExample:
ps aux
Permissions 🔒:
chmod🔑: Change file mode bitsExample:
chmod 755 script.sh
chown👤: Change file owner and groupExample:
chown user:group file.txt
chgrp👥: Change group ownershipExample:
chgrp group file.txt
Networking 🌐:
ping📡: Send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network hostsExample:
ping google.com
netstat🌐📊: Network statisticsExample:
netstat -tuln
ifconfig🌐🛠️: Display or configure a network interfaceExample:
ifconfig eth0
ssh🛡️: Secure shell client (remote login program)Example:
ssh user@hostname
scp📤: Secure copy (remote file copy program)Example:
scp file.txt user@hostname:/path/
Compression/Archiving 🗜️:
tar📦: Tape archiverExample:
tar -czvf archive.tar.gz folder/
gzip🗜️: Compress or expand filesExample:
gzip file.txt
gunzip🗜️🔓: Decompress filesExample:
gunzip file.txt.gz
zip🤐: Package and compress filesExample:
zip archive.zip file1.txt file2.txt
unzip🤐🔓: Extract compressed files in a ZIP archiveExample:
unzip archive.zip
Package Management 📦:
apt-get📥: APT package handling utility (Debian-based systems)Example:
sudo apt-get install package_name
yum📥: Package manager for RPM-based systemsExample:
sudo yum install package_name
dpkg📥: Package manager for DebianExample:
sudo dpkg -i package.deb
Text Processing 🔍:
grep🔎: Search textExample:
grep "pattern" file.txt
sed✂️: Stream editorExample:
sed 's/old/new/g' file.txt
awk📝: Pattern scanning and text processing languageExample:
awk '{print $1}' file.txt
Help & Output 📘:
man📚: Display manual pagesExample:
man ls
echo🔊: Display a line of textExample:
echo "Hello, World!"
Process Management ❌:
kill☠️: Terminate processesExample:
kill -9 12345(where 12345 is a process ID)
❓ Which Linux commands do you find most frequently used in your daily operations?
5. Diagram as Code
Diagrams (Diagram as Code) allows you to create cloud system architecture diagrams using Python.

Originally designed for quick prototyping of new architectures without specialized design tools, it can also be employed to visualize or describe existing systems. The tool is versatile, supporting a wide range of major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes, Alibaba Cloud, and Oracle Cloud, as well as On-Premise nodes, SaaS platforms, and key programming languages and frameworks. One of its standout features is its compatibility with version control systems, enabling you to track changes to your architecture diagrams over time. Note: While Diagrams excels at creating architecture diagrams, it neither manages actual cloud resources nor generates cloud formation or terraform scripts. For a deeper dive, check out the optional 6-minute video below.
❓ Which tool or software are you guys utilizing to generate diagrams programmatically?